Data preprocessing is a critical step in data science tasks, ensuring that raw data is transformed into a clean, organized, and structured format suitable for analysis. A data preprocessing pipeline streamlines this complex process by automating a series of steps, enabling data professionals to efficiently and consistently preprocess diverse datasets. So, if you want to learn how to create a Data Preprocessing pipeline, this article is for you. In this article, I will take you through building a Data Preprocessing pipeline using Python.
What is a Data Preprocessing Pipeline ?
Data Preprocessing involves transforming and manipulating raw data to improve its quality, consistency, and relevance for analysis. It encompasses several tasks, including handling missing values, standardizing variables, and removing outliers. By performing these preprocessing steps, data professionals ensure that subsequent analysis is based on reliable and accurate data, leading to better insights and predictions.
A data preprocessing pipeline is a systematic and automated approach that combines multiple preprocessing steps into a cohesive workflow. It serves as a roadmap for data professionals, guiding them through the transformations and calculations needed to cleanse and prepare data for analysis. The pipeline consists of interconnected steps, each of which is responsible for a specific preprocessing task, such as:
- imputing missing values
- scaling numeric features
- finding and removing outliers
- or encoding categorical variables
By following the predefined sequence of operations, the pipeline ensures consistency, reproducibility, and efficiency in overall preprocessing steps.
How a Data Preprocessing Pipeline Helps Data Professionals?
A Data Preprocessing pipeline is crucial to help various data science professionals, including data engineers, data analysts, data scientists, and machine learning engineers, in their respective roles.
For Data Engineers, the pipeline simplifies work by automating data transformation tasks, allowing them to focus on designing scalable data architectures and optimizing data pipelines.
Data Analysts benefit from the pipeline’s ability to normalize and clean data, ensuring accuracy and reducing time spent on data cleaning tasks. It allows analysts to spend more time on exploratory data analysis and gaining meaningful insights.
On the other hand, Data Scientists and Machine Learning Engineers rely on clean and well-preprocessed data for accurate predictive modelling and advanced analytics. The preprocessing pipeline automates repetitive preprocessing tasks, allowing them efficiently experiment and quickly iterate on their datasets.
Data Preprocessing Pipeline using Python
I hope you have understood what a Data Preprocessing pipeline is and how it helps data professionals. In this section, I’ll take you through how to build a Data Preprocessing pipeline using Python.
A Data Preprocessing pipeline should be able to handle missing values, standardize numerical features, remove outliers, and ensure easy replication of preprocessing steps on new datasets. Now, here’s how to create a Data Preprocessing pipeline using Python based on the fundamental functions that every pipeline should perform while preprocessing any dataset:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
def data_preprocessing_pipeline(data):
#Identify numeric and categorical features
numeric_features = data.select_dtypes(include=['float', 'int']).columns
categorical_features = data.select_dtypes(include=['object']).columns
#Handle missing values in numeric features
data[numeric_features] = data[numeric_features].fillna(data[numeric_features].mean())
#Detect and handle outliers in numeric features using IQR
for feature in numeric_features:
Q1 = data[feature].quantile(0.25)
Q3 = data[feature].quantile(0.75)
IQR = Q3 - Q1
lower_bound = Q1 - (1.5 * IQR)
upper_bound = Q3 + (1.5 * IQR)
data[feature] = np.where((data[feature] < lower_bound) | (data[feature] > upper_bound),
data[feature].mean(), data[feature])
#Normalize numeric features
scaler = StandardScaler()
scaled_data = scaler.fit_transform(data[numeric_features])
data[numeric_features] = scaler.transform(data[numeric_features])
#Handle missing values in categorical features
data[categorical_features] = data[categorical_features].fillna(data[categorical_features].mode().iloc[0])
return dataThis pipeline is designed to handle various preprocessing tasks on any given dataset. Let’s explore how each step in the pipeline contributes to the overall preprocessing process:
- The pipeline begins by identifying the numeric and categorical features in the dataset.
- Next, the pipeline addresses any missing values present in the numeric features. It fills these missing values with the mean value of each respective numeric feature (you can modify this step according to your desired way of filling in missing values of a numerical feature). It ensures that missing data does not hinder subsequent analysis and computations.
- The pipeline then identifies and handles outliers within the numeric features using the Interquartile Range (IQR) method. Calculating the quartiles and the IQR determines upper and lower boundaries for outliers. Any values outside these boundaries are replaced with the mean value of the respective numeric feature. This step helps prevent the influence of extreme values on subsequent analyses and model building.
- After handling missing values and outliers, the pipeline normalizes the numeric features. This process ensures that all numeric features contribute equally to subsequent analysis, avoiding biases caused by varying magnitudes.
- The pipeline proceeds to handle missing values in the categorical features. It fills these missing values with the mode value, representing the most frequently occurring category.
By following this pipeline, data professionals can automate and streamline the process of preparing data for analysis, ensuring data quality, reliability, and consistency.
Now let’s test this pipeline on sample data. You can download the sample data I am using for this task from here. Let’s have a look at the sample data first:
data = pd.read_csv("data.csv")
print("Original Data:")
print(data)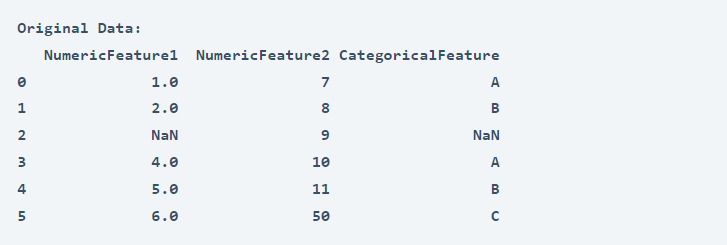
And here’s how you can use this pipeline to perform all the preprocessing steps using Python:
#Perform data preprocessing
cleaned_data = data_preprocessing_pipeline(data)
print("Preprocessed Data:")
print(cleaned_data)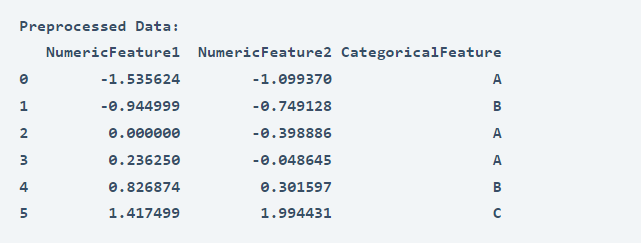
Summary
Data Preprocessing involves transforming and manipulating raw data to improve its quality, consistency, and relevance for analysis. A data preprocessing pipeline is a systematic and automated approach that combines multiple preprocessing steps into a cohesive workflow. It serves as a roadmap for data professionals, guiding them through the transformations and calculations needed to cleanse and prepare data for analysis. I hope you liked this article on how to create a Data Preprocessing pipeline using Python. Feel free to ask valuable questions in the comments section below.

